Determining how much electricity your appliances and home electronics use can help you understand how much money you are spending to use them. Use the information below to estimate how much electricity an appliance is using and how much the electricity costs so you can decide whether to invest in a more energy-efficient appliance.
There are several ways to estimate how much electricity your appliances and home electronics use:
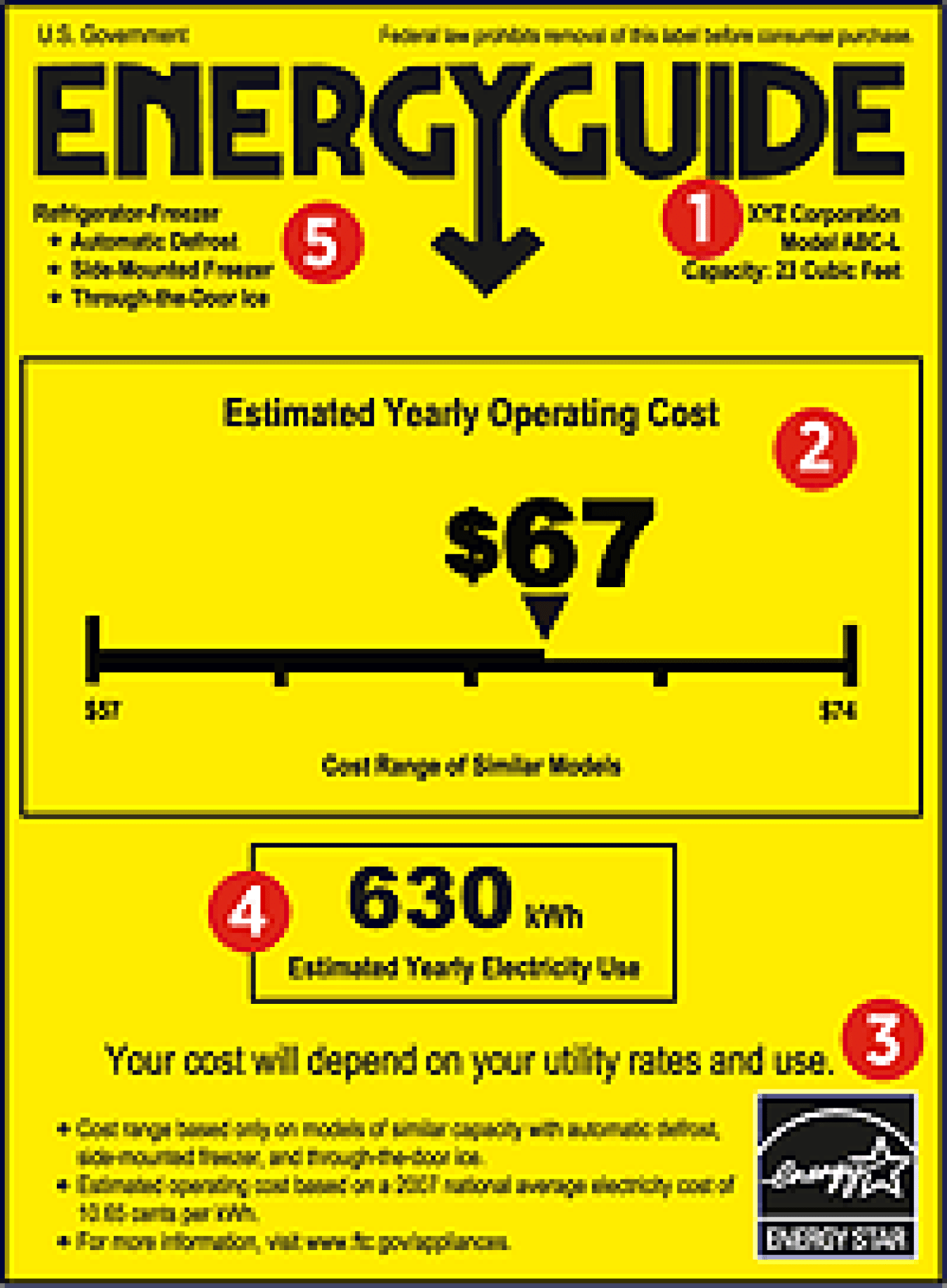
- Reviewing the Energy Guidelabel. The label provides an estimate of the average energy consumption and cost to operate the specific model of the appliance you are using. Note that all not all appliances or home electronics are required to have an Energy Guide.
- Using an electricity usage monitor to get readings of how much electricity an appliance is using
- Calculating annual energy consumption and costs using the formulas provided below
- Installing a whole house energy monitoring system.
Electricity Usage Monitors
Electricity usage monitors are easy to use and can measure the electricity usage of any device that runs on 120 volts. (But it can’t be used with large appliances that use 220 volts, such as electric clothes dryers, central air conditioners, or water heaters.) You can buy electricity usage monitors at most hardware stores for around $25-$50. Before using a monitor, read the user manual.
To find out how many watts of electricity a device is using, just plug the monitor into the electrical outlet the device uses, and then plug the device into the monitor. It will display how many watts the device uses. If you want to know how many kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity the devices uses in an hour, or a day, or longer, just leave everything set up and read the display later.
Monitors are especially useful for finding the amount of kWh used over any period of time for devices that don’t run constantly, like refrigerators. Some monitors will let you enter the amount your utility charges per kilowatt-hour and provide an estimate how much it cost to run the device since it was plugged into the monitor.
Many appliances continue to draw a small amount of stand-by power when they are switched "off." These "phantom loads" occur in most appliances that use electricity, such as televisions, stereos, computers, and kitchen appliances. Most phantom loads will increase the appliance's energy consumption a few watt-hours, and you can use a monitor to estimate those too. These loads can be avoided by unplugging the appliance or using a power strip and using the switch on the power strip to cut all power to the appliance.
Calculating Annual Electricity Consumption and Costs
Follow these steps for finding the annual energy consumption of a product, as well as the cost to operate it.
- Estimate the number of hours per day an appliance runs.There are two ways to do this:
- Rough estimate
If you know about how much you use an appliance every day, you can roughly estimate the number of hours it runs. For example, if you know you normally watch about 4 hours of television every day, you can use that number. If you know you run your whole house fan 4 hours every night before shutting it off, you can use that number. To estimate the number of hours that a refrigerator actually operates at its maximum wattage, divide the total time the refrigerator is plugged in by three. Refrigerators, although turned "on" all the time, actually cycle on and off as needed to maintain interior temperatures.
- Keep a log
It may be practical for you to keep a usage log for some appliances. For example, you could record the cooking time each time you use your microwave, work on your computer, watch your television, or leave a light on in a room or outdoors.

Comments
0 comments
Please sign in to leave a comment.